If you have ever had to import data from multiple sources into one Excel spreadsheet, you know how painful it can be to manually consolidate all that data into a well organized file.
Thankfully Excel has a few “hidden” features that can take away some of the hassle and make the whole process a lot easier.
The Solution
This solution is pretty straight forward and we have created a little example spreadsheet to demonstrate how it is done. You can download the example file containing both the form and the code here.
Open up the spreadsheet and launch the macro. (On the Developer Tab press the Macros button and then press Run)
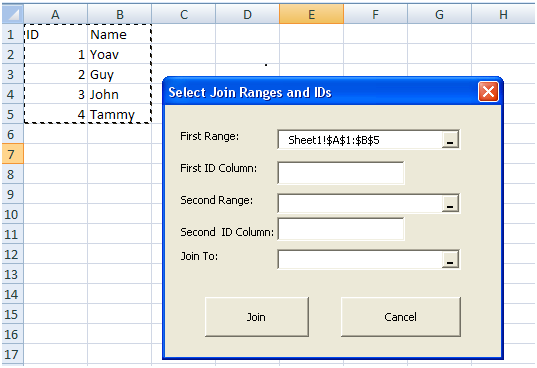
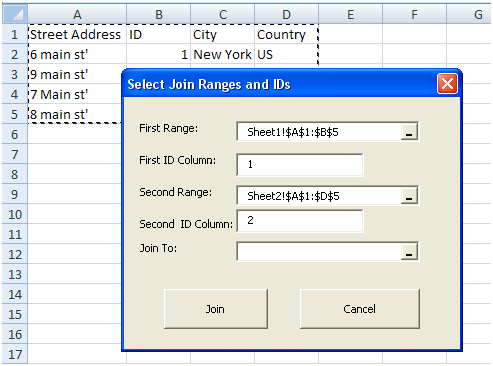
When the data is filled out, the form should look like this:
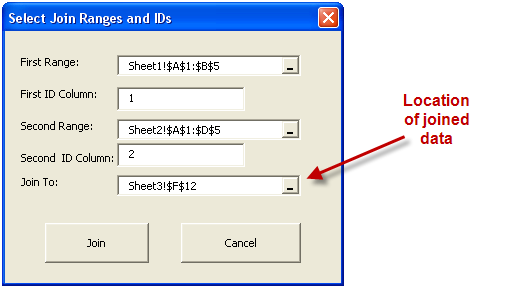
How it Works
The code behind this form is pretty simple and you can adapt it to your needs.
All the work is done by one main subroutine
Sub JoinRanges(rngFirstRange As Range, lngFirstIdColumn As Long, rngSecongRange As Range,
lngSecondIDColumn As Long, rngWriteResultTo As Range)
This routine accepts the ranges, the id columns and the target range (where the data would be written).
The routine copies each line of data from the first range to the target area.
For each line copied, the routine uses the match function to find the matching row in the second function:
Set rngColumn = rngSecongRange.Columns(lngSecondIDColumn) lngMatchingRow = WorksheetFunction.Match(varCurrentId, rngColumn, 0)
Finally we copy the line from the second range (without the id column).
Summary
As you can see, our macro does all the heavy lifting for you. These kinds of repetitive data management tasks can be dramatically optimized with the right spreadsheets, we hope this shows one way your workload can be improved.
P.S.
Don’t forget to check out our PDF To Excel Converter. It can save you a lot of precious time you now spend on retyping PDF data.








